Basic card issuing terminology explained by industry experts

There are many terms and parties involved in issuing a payment card and processing transactions. Below, you can find the answers to most frequently asked questions that will help you learn who is involved in different processes and how card issuing and payment processing works in practice.
What are the existing payment card forms?
The key roles in the payment processing value chain
- What is a cardholder?
- What is a point of sale?
- What is a merchant?
- What is an acquirer?
- What is a card scheme?
- What is an issuer?
- What is a card processor?
Other key definitions within card issuing and payment processing
What are the existing payment card forms?
Most card offerings of today support various card forms, enabling users to pay across online and offline channels. Here are the existing card forms:
- Physical cards, plastic cards as most commonly known, are available today also in a variety of materials.
- Virtual cards – payment cards in a digital form; card details for e-commerce transactions.
- Tokenised cards – cards integrated to digital wallets, e.g. Apple Pay, Google Pay and Samsung Pay.
- Wearables with an integrated payment application – can include smartwatches and rings, for example.
The key roles in the payment processing value chain
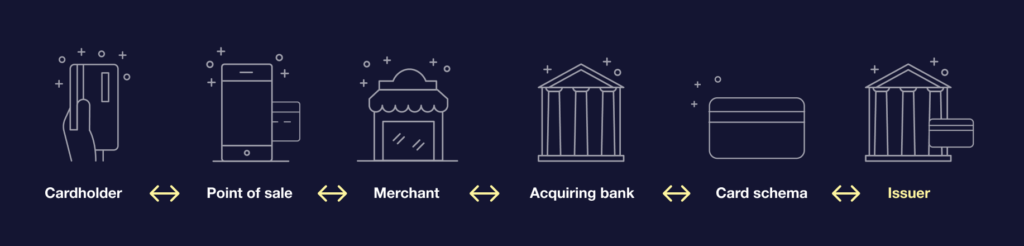
The card payment processing value chain is fairly complex, and there are high barriers to entry. Below, the key stakeholders to a card transaction are outlined – and it is also explained how modern issuers and payment processors interact with those players.
What is a cardholder?
Cardholder means the end-customer using the card to execute a payment. A cardholder applies and receives the card from the issuer, and usually pays some form of service fee for the issuer. Fees may be baked into a subscription service form; alternatively the card can be free of charge but costs of issuing can be indirectly outweighed through increased customer usage, loyalty, and spending.
What is a point of sale?
Point of sale is the location, app or website where a cardholder makes a payment for goods or services. Payment card information is used to forward the transaction to an acquiring bank.
What is a merchant?
Merchant is an entity selling goods or services against payments. Merchants pay a per-transaction fee to the acquiring bank.
What is an acquirer?
Acquirer is a bank or a financial institution processing card transactions on behalf of the merchant. An acquirer routes the payments to the card scheme, receives funds from the card scheme and settles them to the merchant. Acquirers pay an interchange fee for each card payment to the issuer, plus transaction-based fees to the card scheme.
What is a card scheme?
Card schemes are global card payment transaction processors (mainly Visa and MasterCard). They receive payments from acquirers and route them to the issuer. Card schemes partner with card issuers, and with acquirers accepting payments made with those cards.
While the core payment transaction service may be the same, card schemes can have differing segment and geographical focus areas, and offer scheme-specific features and pricing models.
What is an issuer?
Issuers typically maintain the brand, required licenses and the underlying technology required for managing payment cards. Issuer can also be a bank or financial institution with membership to a card scheme which enables card issuing and receives payments routed from the scheme. Issuers pay transaction-based fees to card schemes.
What is a card processor?
A card processor processes the transactions on behalf of the merchant or issuer. The processor receives, processes and forwards data between the card scheme and the merchant or issuer.
Other key definitions within card issuing and payment processing
What is a BIN sponsor?
BIN sponsor is a bank or financial institution with a card scheme membership (Visa or Mastercard). BIN sponsor is the issuer of the card from a legal standpoint, with obligations towards authorities and card schemes for card issuance.
As a regulated financial institution license holder, a BIN sponsor is authorized to hold cardholder funds.
Partnering with a BIN sponsor enables your company to avoid becoming a direct member of a scheme, whilst still controlling the end-customer relationship and the card’s branding.
BIN sponsors differ in terms of pricing, geographical coverage and scope of services
What is KYB/KYC?
Know-Your-Business / Know-Your-Customer. Legislation, especially in Europe, requires the issuers to know who their cardholders are. The process includes identification at the beginning of the customer relationship as well as periodical checks during the customer relationship. The target with KYC/KYB is to mitigate risk related to money laundering and other criminal activity.
What is fraud monitoring?
The purpose of the fraud monitoring process is to minimise the losses for Issuers due to fraudulent card usage and provide safe and frictionless payment experience for cardholders.
What is dispute management?
Dispute Management is to solve issues with the payment transaction and recover losses. Either it is initiated by the cardholder by disputing a transaction or the card issuer cannot support the processed transaction, e.g., no such card account. The requirement for the dispute management may come from the card scheme and/or from the local legislation.
Want to design the ideal payment card solution for your business? Our comprehensive guide has everything you need to know to launch the winning payment card product. Download down below.